
The economics surrounding climate change are a complex area of economics. The financial effects of climate change are difficult to quantify. It is difficult for us to estimate the amount of damage that will occur and how long it takes to solve the problem. We also don't know what the benefits of adaptation or mitigation are. This uncertainty is magnified when the issue is global.
A temperature rise of 3oC is the most common estimate of the impacts of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide emission by doubling it. This range increases would result in an increase of 0.5% of global GDP by midcentury. However, this figure might be lower. Even if the economy were efficient, the cost may be even lower.

Integrated assessment models (IAMs), a type that allows you to include costs from different scenarios, are called integrated assessment models. These models are useful in assessing the effect of a specific policy. IAMs take into account a number of factors, such as technological advancement, economic growth, demographics, and environmental change. The effects on climate policies can be analyzed in monetary terms with an integrated model.
Among other things, a discount rate can be used to capture the social cost of carbon. In this method, the costs of future actions are weighed against the costs of inaction. Depending upon the situation, a discount rates may not give enough weight for future events. The future value of future consumption may depend on the time and the state of nature. Who gets it? In the same way, a discount rate could not reflect catastrophic outcomes like a social collapse.
This uncertainty has led many economists to debate whether it is worth devaluing future actions. They have also noted the importance of accounting for high impact, low probability outcomes. However, the benefits from achieving a target can often outweigh the benefits of not doing so.
While there are still uncertainties about the effects of climate change on the world, the benefits of reducing greenhouse gases emissions are obvious. There are many ways that GHG emissions can be reduced, but technological innovation is the best way to make the transition to lower-carbon economies. Renewable power capacity is forecast to rise 60% on 2020 levels by 2026. Currently, energy generated from renewable sources costs less than that of fossil fuels.
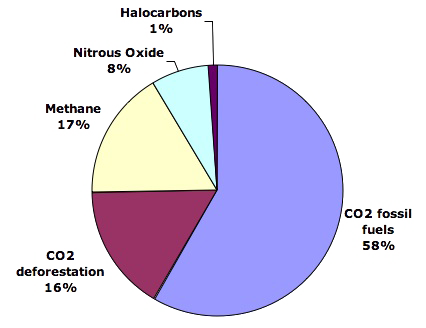
The biggest challenge facing the world is climate change. Many countries have set their sights on net carbon neutrality for 2050. This would require substantial structural changes in the economy as well as capital markets. Nevertheless, the costs of achieving this goal are less than 0.5% of GDP by mid-century.
In fact, it is technically possible to avoid climate change. But there are significant uncertainties and the pace of technological advancement is unpredictable. Furthermore, economic growth is unpredictable.
To address these uncertainties the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC), reported that limiting the warming to 1.5 degree Celsius by 2060 was the most prudent option. Despite the dangers of doing so the international community has committed itself to the 1.5 degree target. The majority of the national governments have committed to this goal.
FAQ
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Due to their limited access to healthcare and technology, developing countries and communities are especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can lead to a decrease in crop yields, which will disproportionately affect poorer communities struggling with food insecurity. Moreover, extreme weather events such as heatwaves and hurricanes can result in the destruction of infrastructure and displacement of people, further perpetuating economic inequality.
Long-term consequences of climate change include increased resource scarcity and poverty as well as health effects such as an increase in vector-borne diseases like malaria or dengue fever. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
What can be done to ensure a sustainable future, given the climate change challenges?
Sustainability means being able to provide for current needs and not compromise future generations' ability. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
It is crucial that we reexamine our consumption and production patterns, as well our dependence on fossil fuels, in order to move towards a sustainable future. We must find new technologies, renewable resources of energy and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our daily needs.
A holistic approach to sustainability is also essential. This means taking into account all aspects of production, from the materials used, waste management, and reuse strategies, to energy utilization in transportation and industry. A wide range of potential solutions exists including the utilization of renewable energies such as solar, wind, and hydropower; better waste management systems; increased efficiency in agriculture; improved transport networks; green building regulations; and sustainable urban planning initiatives.
We need behavioral changes to reach this goal across society. Education programs are necessary to help people understand the climate change issues and how they can make a positive contribution towards a more sustainable world.
Only through cooperation between citizens, business leaders, and governments will we ever be able make substantial progress towards creating a sustainable world for future generations.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate Change has wide-ranging effects on the environment as well society. Climate change can have many effects on the environment. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
The most significant effect of climate change globally is the rise in ocean levels caused by melting ice caps. This results in coastal erosion and increased flooding risks for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events lead to massive destruction of homes, businesses, and even the loss of whole communities. Intense storms increase the risk of flooding and landslides. This can further damage infrastructure like roads, railways, and bridges.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
Many people are forced to flee their homes due to drastic changes in their living conditions.
An increase in aridity means that dust storms can occur more frequently, making people with asthma and other respiratory illnesses like asthma particularly vulnerable. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Climate change is directly affected by land use changes and deforestation. The trees that have been cut down or burned can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of Earth's most important greenhouse gases. This is why less carbon dioxide is removed when trees are cut down or burned for agricultural reasons.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. When forests are cleared for livestock production, the use of fertilizer and pesticides may lead to an increase in methane or nitrous oxide emissions. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. Deforestation can lead to reduced visibility, health issues such as asthma and other respiratory problems. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
How can climate change impact food security and agriculture?
Climate change, global warming, and other factors have direct impacts on agriculture and food supply. The changing climate can impact rainfall patterns and temperatures as well as soil moisture levels. Extreme weather is also possible. This can cause disruptions in farming, decrease crop yields, and result in a loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures could lead to the growth of pests or diseases, which can have a negative impact on crops. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. The changing climate can also affect livestock production. High temperatures in summer months can decrease fertility rates in animals such as cattle, sheep, or goats. This can lead to lower milk yields that can increase food insecurity in communities.
Global warming and climate change have a complicated relationship. However, adaptation strategies are being implemented by governments globally through strategic investments made in climate-smart farming (CSA). This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. It is essential to make improvements in existing infrastructure so that appropriate actions may be taken when crucial crop thresholds are reached. This includes the introduction of stable irrigation networks with adequate access waters at times when there is less availability due to warmer temperatures or heavy downpours, which can wash away important access water resources. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
How is extreme weather related to climate change
Extreme weather events, such as heat waves, floods, droughts, cyclones, storms, and hurricanes are directly linked to global warming. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
According to climate scientists the average frequency for extreme weather-related events has increased more than twofold since 1980. Rising ocean water temperature causes sea levels to go up as well as changing wind patterns. This impacts the normal distribution of storms or hurricanes in different areas across the globe.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Several places including Antarctica have recorded their highest-ever temperatures indicating a definite relation between global warming trends and the occurrence or frequency of extreme weather events around the world.
Another example is Hurricane Irma, which struck in 2017, causing $50 billion in economic damage not only to Florida, but also to other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba, and others. This proves once again that climate change has been responsible for an increase in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change concluded that humans are increasing the severity and frequency of climate change. This naturally leads to more severe, frequent, and intense natural catastrophes worldwide. It also provides strong evidence about human involvement in extreme weather events that occur at regular intervals around us all.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Educate your Community about Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Climate change education can be in many forms, from online resources and interactive educational tool to classroom activities, simulations, experiential learning programs, and classroom activities. The key elements of effective climate change education are:
-
arming people with practical knowledge about the subject
-
Demonstrating the many ways individuals can make positive changes
-
Engaging participants in an open discussion about possible solutions
-
Inspiring action through shared experiences
Teachers can help communities to reduce their environmental footprints by offering comprehensive lessons in climate change for both adults and students.
A unique way to engage people in meaningful dialog is to link scientific research with real world examples. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
By incorporating action-oriented activities into education curriculums, participants are equipped with the mental tools necessary to create campaigns or petitions. They can then become agents of change in their communities or for sustainability. Individual agency is important because it highlights the importance to reduce emissions. Participants can also be shown how they contribute collectively towards a better outcome. Involving stakeholders early in the decision-making process encourages them to be involved. This could lead to more equitable outcomes for all those affected by policy design decisions. We might be able, together, to increase public awareness of the effects of climate change and take appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.