
Resilience is an important factor in managing climate change's impacts. Resilience is the ability of a system or organization to adapt to dangerous events. It often centers on the resilience of buildings stock. These efforts aim to reduce risks associated with buildings, supply chain, and other infrastructure. These efforts are usually carried out by policy makers and decision-makers. However, resilience can be difficult to achieve. This article will explain how resilience is defined, implemented, and measured in the building industry. These insights help stakeholders to identify adaptation opportunities and make informed decision.
A variety of academic fields have been studying climate change resilience. In particular, cities have been the focus of resilience research. These strategies include increasing the resilience of buildings to specific hazards like flooding and seismic activity. Additionally, these strategies seek to reinforce emergency responses, and reduce the recovery time frame.
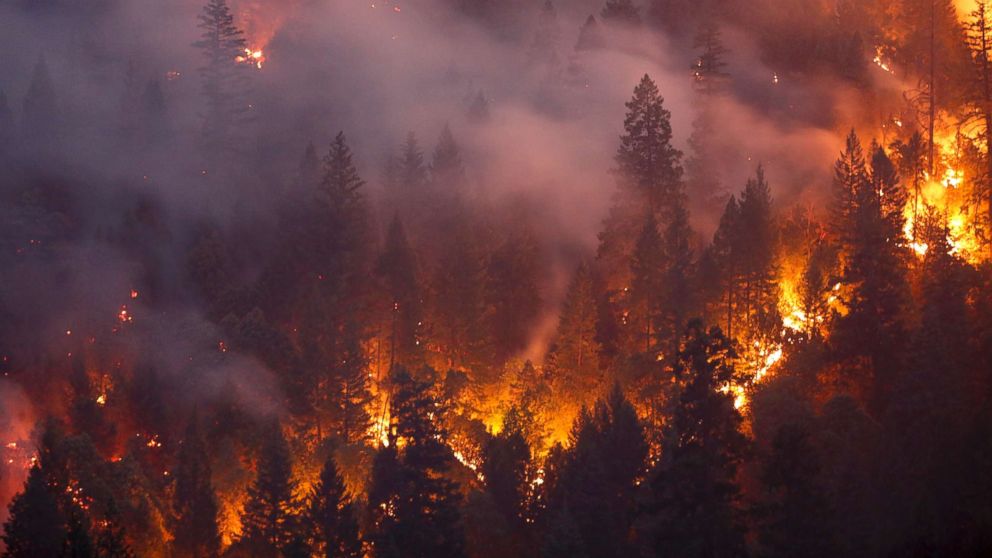
Resilience is defined as the ability to maintain essential processes and structures by ecological research. A resilient built environment is one that can withstand extreme natural hazards such as hurricanes and floods. It can also reduce human-caused dangers like wildfires. Although this definition is simplistic, it accurately reflects current knowledge about resilience.
Resilience in Social Science is another area that we are interested in. This domain addresses the interplay among system components, such communities, and identifies important roles for government and business. One resilience strategy involves strengthening social cohesion and community empowerment. Even though it is not as well-known, it suggests an important need to adapt.
Other resilience strategies involve the development of alternative interventions, such as solar panel kits. These might be cheaper than rebuilding, especially in low resource settings. However, these techniques come with limitations. They may not be applicable in remote and difficult to access areas.
Efforts to strengthen climate resilience are also characterized by their diversity. The Northern Institute of Applied Climate Science for example has incorporated traditional ecological wisdom into its research. There are also various international coalitions dedicated to resilience, such as the Adaptation Research Alliance. All of these initiatives are designed to share best practices, develop metrics, and mobilize countries.

A third major area of focus is finance. Through the Executive Order on Tackling Climate Crisis, the United States is trying to increase resilience finance. This includes coordination among different departments and agencies. In the same vein, the United Kingdom will place additional emphasis on adaptation in 2021 at the G7 Summit.
There is also a solid literature in the social sciences on resilience, which addresses climate change response factors. Some studies have focused on resilience theoretical frameworks. Others have investigated the effects of resilience and economic well-being. While the majority have focused on disaster-risk reduction, other resilience strategies are being explored in social science.
As resilience approaches and strategies continue to develop, it is important to understand how different definitions of resilience impact professional practice. Understanding the meanings of resilience can help stakeholders decide the best approach to a particular situation.
FAQ
What are the international efforts currently being made to address climate change
The current state of international efforts to address climate change is one of unprecedented unity and momentum. International efforts to address climate change are being facilitated by countries around the world, who are increasingly working together to reduce carbon emissions, improve resilience and invest in renewable energies.
The Paris Agreement has been a catalyst for global action. Individual countries can set voluntary targets for reducing their carbon emissions by using the framework provided by the Paris Agreement. In addition, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change provides political guidance as well as piloting new initiatives such carbon market mechanisms.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
The OECD committee represents wealthy countries and has established common standards for reporting national climate action through the Common Reporting Framework, also called the 2021 Guidelines.
These efforts signify a new level of importance for climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
What are the causes for climate change
Climate change is a global phenomenon that has been driven by an increase in human-generated greenhouse gases emitted into our atmosphere, primarily due to fossil fuel burning for electricity and transportation. These greenhouse gases trap more heat from the sun, which causes global warming.
Climate change is also caused in part by human population growth, the destruction and clearing of ecosystems, energy consumption and overgrazing. This also reduces the number naturally occurring carbon sinks, which absorb CO2 from atmosphere. Natural forces such as changes in solar radiation can also contribute to climate change.
These human activities together result in Earth experiencing an overloading of its energy budget. This has caused an average global rise of 1° Celsius over pre-industrial time. Glaciers melt quicker than they form, and sea levels rise because oceans absorb most the heat energy. Other damaging consequences include water scarcity and droughts or extreme weather events like floods and hurricanes caused by frequent heavy precipitation on saturated soils.
It is vital that we reduce our carbon footprint immediately and stop releasing greenhouse gases. This will help us protect ourselves against further damage from climate change. It is essential to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels in order to produce electricity. This can be done alongside investing in renewable energy sources such as wind turbines and solar panels, which emit no harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. Reforestation and other sustainable practices can help restore balance to these delicate planetary cycles that we depend on for our survival.
What is the potential of new technologies to combat climate changes?
The potential of new technologies to address this global challenge is vast. The advancements in applied science allow us to make a transition to a sustainable future.
New methods for carbon capture or sequestration can be used to lower greenhouse gases. Additionally, improved agricultural practices can reduce the emissions of livestock and soil erosion. Smart grid technology is also possible to be integrated into existing power infrastructure, resulting in an efficiency boost. Furthermore, improved building design can help decrease energy consumption.
Additionally, scientists can develop organisms using cutting-edge synthetic biological approaches to convert green sources of fuel like CO2 lasers into usable biofuels or alternate feedstocks. This could be a major shift in transportation if there is a shift away from petrol-based vehicles to electric cars powered solely by renewable sources.
Finally, increased investments in digital technology or AI can provide people with more information on their ecological footprints across borders. This will allow them to make more informed decisions regarding their consumption habits. Understanding our contribution to carbon production is crucial for us all to be better stewards.
How can the world make a transition to a more sustainable future given the challenges presented by climate change?
Sustainability is the ability for future generations to meet their current needs without compromising their ability to do the same. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
We must reexamine how we consume and produce energy, as well as our dependency on natural resources like fossil fuels, if we are to make a transition towards a more sustainable future. We must seek out new technologies, renewable sources of energy, and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our everyday needs.
It is important to adopt an integrated approach to sustainability. This involves considering all aspects of production from materials used, waste management and reuse strategies to energy use in transportation and industry. There are many possible solutions, such as the use of renewable energy like solar, wind, or hydropower; better waste management; increased efficiency of agriculture; improved transport networks; green construction regulations; and sustainable city planning initiatives.
This goal requires behavioral changes from individuals in all sectors of society. Education programs are essential to assist people in understanding the impacts of climate change. They can also help them understand how they can contribute positively to a more sustainable planet through micro-actions like reducing food waste and adopting low-carbon lifestyles.
Collaboration between government leaders, industry leaders, as well as citizens is the only way to make significant progress toward creating a more sustainable future for our children.
How does climate change politics impact global efforts?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It has been difficult to reach a consensus on the global effort to address this urgent environmental problem.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. These issues are often subject to political interference that can hamper global cooperation in order to implement sustainable energy practices, preserve natural habitats, find viable technological solutions and other interventions related to climate change.
Most governments are eager to protect their business interests and enforce rules that will limit business activity as much as possible. This is often in conflict with the regulations experts recommend to combat climate change. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with greater economic power are more likely to elect their own representatives to the international bodies responsible for negotiations on the environment. This can cause lopsided discussions about the interests of each country versus the collective interest all parties. Additionally, the potential side effects of implementing radical changes like geoengineering are being heavily debated at both national as well international levels.
A grassroots movement has also struggled against powerful opposition, including corporate ownerships as well-funded lobbyists trying to keep their industries politically favorable. This is especially true when it comes funding research into alternative energy production and enforcing mandates for renewable energy technology. Individual governments need to be clear about the potential rewards and outcomes of making valid progress on the issue. They cannot seek short-term spectacles or gains to gain public support.
If we are to achieve a coordinated effort to address our current environmental crisis, it is crucial to properly distribute resources and be aware of political divisions among nations.
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes have already had a significant impact on ecosystems across the globe, leading to habitat loss and extinction. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
The number of extreme weather events - such as cyclones, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires - has been steadily growing over time due to higher average surface temperatures caused by human activity. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. To prevent further destruction and devastation caused by climate change, all countries must work together to take immediate action and plan for adaptation in an ever-changing world.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Educate your Community about Climate Change and Mobilize Action
You can learn about climate change through many different methods, from interactive online tools and educational resources to classroom activities and simulations to experiential learning programs and classroom activities. These are the essential elements of effective climate education:
-
The goal is to provide practical knowledge and skills for the people who are interested in this subject.
-
Demonstrating the many ways individuals can make positive changes
-
engaging participants in open dialogue about potential solutions
-
Inspiring action through shared experiences
Educators will be able, through comprehensive lessons on climate change that are accessible to both students and adults, to help their communities create strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
Connecting scientific research and real-world examples creates a unique opportunity to engage audiences in a meaningful discussion. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
Participating in action-oriented activities within educational curriculums gives participants the mental tools they need to create campaigns, form petitions or take local actions. This empowers them to become agents for social and/or political transformation or sustainability improvement. Individual agency is important because it highlights the importance to reduce emissions. Participants can also be shown how they contribute collectively towards a better outcome. Involving stakeholders early in the decision-making process encourages them to be involved. This could lead to more equitable outcomes for all those affected by policy design decisions. With concerted efforts to increase public understanding of climate change and taking appropriate action to limit greenhouse gas emissions, it might be possible to create an environment where these urgent matters can be addressed quickly with attention given where needed most. Together we may be able one day to ensure that successful implementation measures will be put in place that will help us all reach our collective goals.