
Droughts are getting more frequent and severe due to climate change. They affect crops and livestock, and are a threat to the food supply. They can also lead to water shortages which can be harmful for the environment as well as public health.
Droughts can happen in many places. They can last for many years or even decades. They also come in a variety of severity levels, from very mild to very severe. A drought is the absence of precipitation for prolonged periods. There are many reasons that drought can occur, including human activities and extreme weather. These and other factors can have a negative impact on crop yields, as well as the production process.

Droughts can be a natural occurrence or caused by a human-generated greenhouse gas emission. The latter is more common and is associated both with higher temperatures and decreased rainfall as well as the evaporation and evaporation.
The soil loses its moisture when it isn't getting enough rain. This affects the availability of water for crops during warmer months. During periods of low moisture, trees and shrubs die, rangelands become saline, and wildlife dies. Wildfires can cause severe damage because the vegetation has no place else to go. Research suggests that climate change could be contributing to the increase in droughts.
Droughts are becoming more common due to changing weather patterns and ocean temperatures. Storms, like those mentioned above, are developing closer to the poles and changing direction. The Gulf of Mexico is heating and the jet stream is moving to the south. This allows moisture to flow from the Gulf to Great Plains. These changes are still not fully understood.
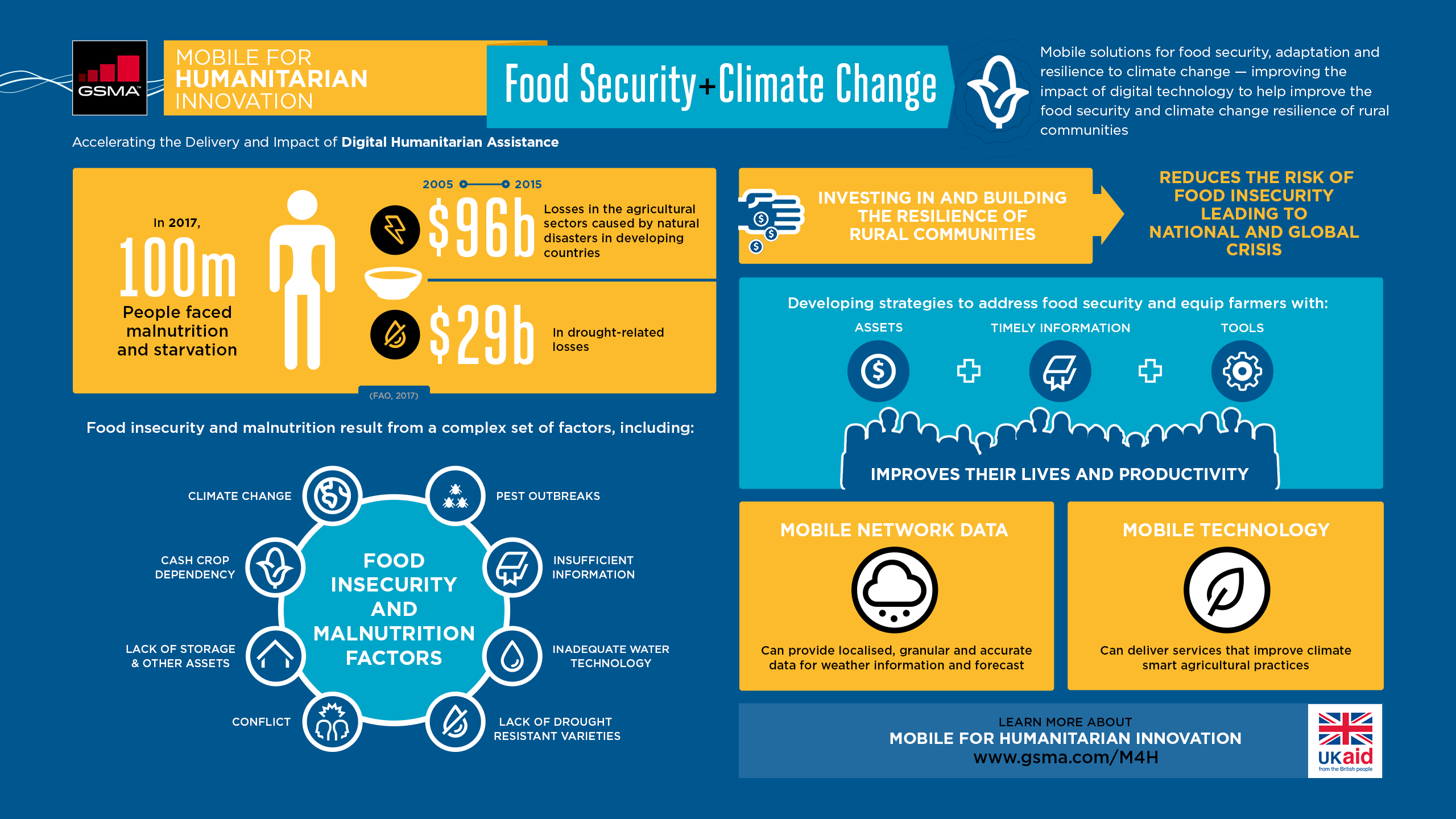
Another study found that the probability of co-occurring droughts increased substantially in the 21st century. These simultaneous droughts can have devastating consequences on global food security. The impact on agricultural output could be severe, and the price of food can increase.
Droughts can be unpredictable but scientists are confident that climate change will cause them to increase. The Palmer Drought Severity Index predicts future stress for 70% of the world's land area. As a result, this number will increase by 1.7x.
Droughts are more severe in developing countries, especially Latin America. Low rainfall is causing crop damage. In addition, underground aquifers are draining their water faster than it is refilling, which can lead to further destruction of crops. This has led to farmers being forced from their land. Many people have been affected by political unrest and food riots.
Globally, there has been a marked increase in the frequency and severity of droughts. Fossil fuel use and human-generated warming are both key contributors. A recent study shows that 46% is due to human-generated heat.
If we continue to produce more carbon dioxide, the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases will rise further. This will make drought even more dangerous. Researchers have made it clear that the link between human-caused warming and droughts does not exist. There are other factors that can contribute to droughts.
FAQ
How can the energy sector be involved in climate change?
The energy sector is a major contributor to climate change. The main source of global warming comes from the burning of fossil energy. It releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, traps heat, and results in an increase on Earth's average temperature.
This is why energy sources need to shift away from carbon-emitting resources like coal and natural gas and instead switch towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and geothermal. This transition can be made through both government policy and incentives, as well as investments in innovative technology like hydrogen fuel cell. Businesses and homeowners can cut their emissions while reducing their electricity bills by investing in infrastructure that supports these renewable sources.
Other options include switching away from petroleum-fueled cars, moving towards electric vehicles, and public transport. Governments have the power to encourage and support investment in cleaner modes for transportation.
Companies must also adopt green business practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing better insulation in offices and implementing energy efficiency plans at production plants. This can drastically reduce operational expenses while also improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives must not only be supported at the company level, but also at the federal level to be truly successful. Taxing pollution products increases individuals' willingness to adopt healthier practices. But this won't force them to compete with polluters. Instead, vouchers or subsidies for low carbon products will create a continuous market to support sustainability. The private and public sector must work together to combat climate change. Providing vouchers or subsidies for low-carbon products and switching to cleaner energy sources will create a market that supports sustainability efforts.
What role does climate change play in greenhouse gas emissions?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them the planet would be much more colder than it currently is.
These greenhouse gases are created by human activity such as burning fossil fuels. These activities increase the heat that is trapped in the atmosphere. This leads to higher temperatures and more extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Due to human activities, the concentration of greenhouse gasses has increased dramatically since preindustrial time. Global warming has caused an increase in temperature all around the globe, and in our oceans. It is also causing changes such as more intense storms and droughts, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. Climate change is affecting ecosystems and wildlife today.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Changes in the hydrological cycle can also affect water availability for aquatic species.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. Climate change could lead to the extermination of up to 30% of animal species by 2050. This would cause further ecological community losses.
Climate change is an enormous threat to biodiversity and to human societies which depend on functioning ecosystems. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change refers the long-term shifts that occur in global weather patterns due to an increase in greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which causes global temperatures rise. This leads to many changes in weather and climate. These can include rising sea level, melting glaciers or droughts, widespread coral bleaching, species extinction and disruptions in food production.
Climate change is primarily caused by human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, transportation, and cutting down forests. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. It releases the stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when trees are chopped down or burned. Additionally, forests act as a natural carbon sink that removes CO2 from the air; without this absorptive capacity, carbon dioxide levels will continue to rise with devastating consequences for ecosystems around the world.
The release of CO2 into the atmosphere is not the only effect of human-caused polluting. Other harmful gasses like methane, CH4, and nitrous dioxide (N2O), are also emitted by humans. Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
Humanity must work together across all levels of society, economy, and politics to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We need to shift from dependence on fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and low-carbon hydrogen fuels in order to limit climate change. The smart solution to reduce CO2 accumulation and atmospheric pollution could be replacing polluting fossil energy sources with zero-waste solutions. By taking responsibility for our impact on our environment we can begin mitigating damage through preservation measures like reforestation projects which help maintain biodiversity while absorbing large volumes of damaging CO2 back into nature providing powerful assistance in addressing the climate crisis and restoring balance for future generations
How do developing countries and communities experience the effects of climate change?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can result in a reduction in crop yields. This will be disproportionately detrimental to poorer communities who are facing food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
The long-term impacts of climate change include resource scarcity, poverty, increased health risks, and an increase of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever. There will also be an increased risk of flooding from rising sea levels, combined with extreme weather events. This puts lives at risk in coastal locations where many people lack the necessary infrastructure and emergency services to evacuate. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate-Friendly Policies and Companies
Individuals have many options to support climate-friendly policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can take practical steps like switching to greener providers or choosing more sustainable products than those that emit higher carbon emissions.
A key step to supporting climate-friendly policies is reducing one's carbon footprint. This may include changing daily habits such unplugging electrical appliances and switching off lights when not required, using environmentally friendly household products like biodegradable cleansers and composting kitchen soiled food scraps rather that putting them in landfills, wearing sustainable fiber clothing, choosing local foods whenever possible, installing energy-efficient energy systems at your home with solar panels or wind turbines, as well as planting trees around the property that absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
Investors interested in supporting climate friendly policies should research companies with lower carbon emissions before investing. Additionally, they should look into their portfolios periodically to ensure they meet the sustainability standards they have set themselves ahead of time. Investors may want to ensure that their investments in Green bonds do not finance projects with any activity which contributes more greenhouse gases into the air than they take away. Investors should look out for opportunities to use funds towards green business activities. This includes renewable energy alternatives, community-building projects, and initiatives that promote sustainability.