
The main impact of climate change is the rise in sea level. It affects both the physical and chemical characteristics of the ocean. Although scientists agree that global water levels will increase over the next century, there are still many options for mitigation and adaptation. This article will look at some of those options.
Many studies have shown that ocean temperatures have increased since the Industrial Revolution. A rising amount of CO2 in our atmosphere is also contributing towards the warming of the sea. The ocean and climate change are directly linked. The Antarctic is melting water, which is driving up the rate at which sea levels rise. The Greenland glacier sill is being eroded by warmer water. Coral disease is also on the rise due to rising temperatures. Climate change also has other effects, such as an increase in hypoxia and dead zones.
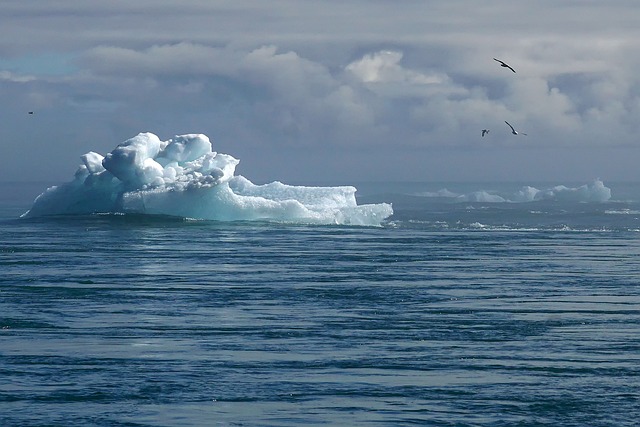

Sea-level rises could pose a threat to coastal cities, the water infrastructure and public health. The sea-level will rise to 60 to 110 cm in 2100 if greenhouse gas emissions continue to increase at the current rate. Some estimates suggest that the sea-level average will reach two meters within the next century. To predict the future, however, it is necessary to conduct more research.
Changes in Atlantic Ocean circulation can be associated with changes at sea level. This is most likely due to the melting Antarctic Ice Sheet. Sea-level increase can also be caused if there is warmer water to the north. Sea-levels around the world have risen six to eight inches in the past 20 years. More research is needed to determine the extent and cause of these changes.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released a special report on cryosphere. This report gives a comprehensive look at the impact of climate change upon the ocean and cryosphere. It was produced by a group of 100 scientists from 36 countries. One of its findings is evidence that Arctic permafrost has begun to thaw on a monthly base.
The Fifth Assessment Report of the IPCC is another report that examines the impact of climate change upon marine ecosystems. These changes are driven by changes in oxygen, salinity, and other nutrient inputs, as well as shifts in marine ecosystems and circulation.
The rapid emission of greenhouse gases has caused many of the changes observed in the past 40 years. These include the rise of sea level and acidification. The increase in planktonic diversity and volume is due to climate and temperature change. This has led to a shift in the distribution of these species. The result is a change in the food web. This has led to an increase in the incidence of disease and a decrease in the abundance of habitat-forming species.
A new study has shown that the ocean acts as a powerful moderator for Earth's climate system. Despite the complexities of ocean-climate interaction, a number of important advances in science have been made. Blue carbon, or carbon dioxide taken from the ocean and stored within sediments, is one example. Using this technology could provide a long-term method of carbon storage.
FAQ
What is the role that individuals and groups can play in addressing climate-change?
Climate change is one of the biggest contemporary challenges we face today. It affects all of us and requires our collective attention as well as individual actions to make a real difference.
Individuals have an essential role to play in addressing climate changes and reducing their effects. Everyday behaviors can include anything from reducing waste and consuming consciously, going through changes in lifestyle such as switching to a vegetarian diet, consuming less meat, using public transportation more often, and choosing more sustainable materials in clothing and home decor. They can also take part in advocacy and support initiatives that promote sustainability in their communities.
The key to addressing climate change at a larger scale is also the role of communities. They can create policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions by encouraging electric or bicycle transport, deforestation reductions, and the promotion of composting. Collaboration between different communities across cities and countries is fundamental for achieving success in this mission.
This will help individuals become aware of the issues at stake and understand how to contribute positively to tackling them. This will help people become more aware about the issues and to understand how they relate to others who are also affected by global climate change.
Employers have a significant responsibility in combating climate change. Introducing corporate practices that are focused on sustainability and choosing green alternatives whenever feasible will undoubtedly result in positive economic and sociological outcomes.
Therefore individuals' actions plus community-wide policies together with business transformation will contribute immensely towards creating solutions against global warming and collectively defending humanity against longer terms harmful effects growing out from climate change.
What are the main causes of climate changes?
Climate change, which is a global phenomenon, has been driven by an increased amount of greenhouse gases from human activity. The increase was primarily caused by fossil fuel burning to generate electricity and transport. These emissions lead to a greater amount of sun's energy being trapped in Earth’s atmosphere, which results in rising temperatures.
Other factors contributing to climate change include population growth, land clearing and destruction of ecosystems, deforestation, energy consumption, and over-grazing. This further reduces the number of naturally occurring carbon sinks that absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. Climate change can also come from natural forces, such as changes in solar energy.
These combined human activities result in overloading Earth's capacity to properly balance its energy budget, leading to an average increase of 1 degree Celsius globally since pre-industrial times. Because oceans absorb the majority of heat energy, glaciers are more likely to melt than they ever form. Other negative consequences include water scarcity, droughts and extreme weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
To avoid further damage, it is crucial that we reduce carbon emissions and take steps to curb our emissions. This will give us a fighting chance against climate change's already serious impacts. It is essential to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels in order to produce electricity. This can be done alongside investing in renewable energy sources such as wind turbines and solar panels, which emit no harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. You can also restore some balance in these delicate cycles of the planets that sustain us, such as reforestation.
What is the current state of international efforts to address climate change?
The current international climate-change effort is moving forward with unprecedented momentum and unity. Countries around the world are increasingly collaborating on ways to reduce emissions, strengthen resilience against impacts, and invest in renewable energy sources.
The Paris Agreement has been a catalyst for global action. Individual countries can set voluntary targets for reducing their carbon emissions by using the framework provided by the Paris Agreement. Additionally, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is providing political guidance and piloting new initiatives such as carbon market mechanisms.
In certain regions, there is progress as well. The European Green Deal, for instance, is a comprehensive set of legislation that aims to rebuild Europe's economy while African countries have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative. This Initiative aims to increase Africa’s global share of renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
Through the Common Reporting Framework (CFR), the 2021 Guidelines, the rich countries that are members of the OECD committee have agreed to common standards for reporting their national climate change actions.
All these efforts are a sign of the unprecedented importance given to climate action. If we are to meet the Climate goals as set out by science and enshrined into international law, governments, civil society, and private sector stakeholders must all continue to build on this momentum.
What is the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change has many effects on biodiversity and ecosystems. Climate change is affecting ecosystems and wildlife today.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. The hydrological cycle changes can have an impact on the availability of water for aquatic species.
Climate change also causes rising temperatures, more frequent extremes like droughts and flooding. This puts additional stress on fragile systems like coral reefs and tropical rainforests. The climate change will lead to the extermination or decline of as many as 30% of animal species in 2050. This could cause further destruction of ecological communities.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. To mitigate its effect efforts must be made at all levels to reduce global warming trends and future damages should be avoided where possible with careful management practices.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
Human activity can cause greenhouse gases, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other industries that emit emissions. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These actions will reduce the atmospheric concentrations and improve the environment for all living things on Earth.
How will climate change impact the world's oceans?
What is the impact of climate change on the world's oceans and marine life?
Since its inception, climate changes have had significant impacts on the oceans of the world and the marine life that surrounds them. Constant oceanic warming due to the depleted ozone layer causes drastic disruptions in marine ecosystems resulting in a decrease in species and coral bleaching.
Unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms are also linked to climate change, leading to extreme surges in sea levels that can prove deadly for coastal areas. Furthermore, changes in temperature may reduce oxygen levels in water systems resulting in "dead zones" where abundant marine life becomes sparse.
Climate change is also contributing to ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere that accumulates within the oceans. Ocean acidification raises the pH balance which disrupts essential functions of animals unable to adapt such as oysters, clams, and crabs as their shells become weakened.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. Ocean stress increases already high extinction rates worldwide, creating a severe imbalance of predators and prey which might lead eventually to complete extinction.
All ecosystems are affected by climate change. This can be directly or indirectly via evaporation, water volume reductions or sharp temperature shifts. These changes could have a devastating effect on sustainable development of marine activities and fisheries. Climate change is transforming the future of all life forms on our planet, not just those living on land but those living below the ocean surface.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Educate Your Community About Climate Change and Mobilize Action
Many forms of climate education are available, including interactive educational tools and online resources, as well as classroom activities, simulations, or experiential learning programs. The following are key components to effective climate change education:
-
arming people with practical knowledge about the subject
-
Demonstrating how individuals can make a difference
-
Participants are invited to engage in an open conversation about possible solutions
-
Shared experiences inspire action
Educators will be able, through comprehensive lessons on climate change that are accessible to both students and adults, to help their communities create strategies for reducing their environmental footprint.
Furthermore, connecting scientific research to real-world examples is a great way to engage audiences in a meaningful conversation. Participants also have the opportunity to observe positive outcomes and learn from them, which can lead to further innovation or replication within their organizations.
Participants are empowered by incorporating action-oriented activities in educational curriculums. This gives them the mental tools needed to create campaigns, petitions, and take local actions. It also allows them to be agents for social and political change or sustainability improvement initiatives. A focus on individual agency emphasizes the importance and benefits of participation in reducing carbon emissions. However, it also highlights participants' collective contribution to a larger end result. Participating early in policy-making helps to encourage active participation. This allows for more equitable outcomes. We might be able, together, to increase public awareness of the effects of climate change and take appropriate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.